Electricity is a fundamental part of modern life, powering everything from home appliances to industrial machinery. When it comes to supplying power to homes, businesses, and factories, the primary distinction lies in whether the power is provided through single-phase or three-phase electrical systems. Understanding the difference between single-phase and three-phase is crucial, especially when choosing the right power supply for different applications. In this article, we will explore the differences, advantages, applications, and technical aspects of single-phase and three-phase systems.
What is Single Phase?
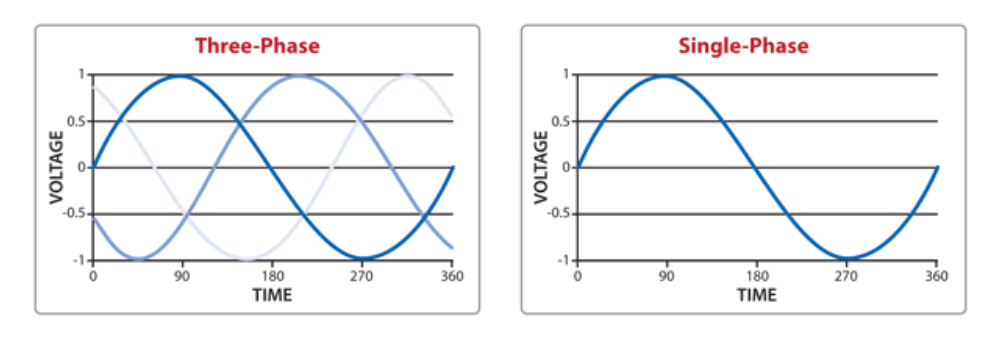
Single-phase electric power is a type of AC (alternating current) power system that consists of two wires: a phase line and a neutral line. In most cases, there may also be a ground wire, but it is not necessary for the functioning of the system. The voltage in a single-phase system varies in a sinusoidal manner, and typically, this power is used for residential or light commercial applications.
In single-phase power, there is one alternating voltage waveform that changes direction periodically, providing power to electrical devices. The power supply works on the principle that electrical energy is delivered through a single alternating current that varies with time.
Applications of Single Phase Power:
Residential homes
Small businesses
Household appliances (refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, etc.)
Single-phase systems are cost-effective for small power requirements and are commonly found in areas with lower energy demand.
What is Three Phase?
Three-phase power is a more complex and efficient method of transmitting electrical energy. It consists of three alternating current (AC) power lines, each of which carries a sinusoidal waveform. These three waveforms are all equal in magnitude and frequency but are 120 degrees out of phase with each other. This phase difference ensures that the power supply remains continuous, providing a smoother flow of electricity.
The power in a three-phase system is more stable than single-phase, and it is able to handle much higher loads more efficiently. Each phase in the system delivers a separate voltage waveform, and the sum of these voltages provides a consistent supply of power. This continuous flow of power is particularly beneficial for large-scale industrial machinery.
Applications of Three Phase Power:
Industrial facilities
Large-scale commercial operations
High-power equipment (motors, compressors, large pumps, etc.)
Large-scale electric power transmission
Key Differences Between Three Phase and Single Phase
Power Supply and Efficiency
One of the primary differences between three-phase and single-phase power is the power supply. In a single-phase system, the power is provided by a single alternating current, which means there are only two wires: a phase line and a neutral line. This system is best suited for smaller applications where the demand for electrical power is not excessive.
In contrast, a three-phase system consists of three alternating currents, with each current flowing through a separate wire. The three-phase power supply provides more constant and stable energy compared to single-phase, making it ideal for larger, more power-hungry applications. The three-phase system offers several advantages, including the ability to transmit more power with fewer wires and greater efficiency.
Cost of Generation and Transmission
The cost of generating and transmitting three-phase power is generally lower than that of single-phase power, especially when the power demand is high. For example, three-phase generators and transformers are typically less expensive to produce than single-phase generators with the same power capacity. This is because three-phase power uses fewer wires to transmit the same amount of energy, making it more efficient in terms of both material costs and energy consumption.
Table: Comparison of Generation and Transmission Costs
| Feature | Single Phase | Three Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Wires | 2 | 3 |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Generation Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Transmission Cost | Higher | Lower |
Power Delivered
Another significant difference is the amount of power that can be delivered. In a single-phase system, the power fluctuates, meaning that there are periods when the power delivery is zero. On the other hand, three-phase power is continuous and can deliver a constant amount of power, making it more reliable for industrial and large-scale applications.
In terms of efficiency, three-phase motors deliver more power using less energy compared to their single-phase counterparts. This is why three-phase motors are used in industries where high power is needed for machinery and heavy equipment.
Motor Size and Capacity
The size and capacity of motors in three-phase systems are typically larger than in single-phase systems. For example, a three-phase motor can be up to 50% more powerful than a single-phase motor with the same material. This difference in capacity makes three-phase motors ideal for applications that require a high amount of mechanical power.
Applications of Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Motors:
Single-phase motors are commonly used in household appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, and fans.
Three-phase motors, on the other hand, are used in industrial machines like wind turbines, belt conveyors, hoists, compressors, pumps, and other heavy machinery.
Voltage Requirements
The voltage supplied by a single-phase system is typically lower than that of a three-phase system. In most countries, single-phase systems supply 120V or 240V, while three-phase systems operate at higher voltages such as 400V or 415V. This is why three-phase power is more efficient for transmitting larger amounts of energy over longer distances.
Table: Voltage Comparison
| Power Type | Voltage Range | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Single Phase | 120V - 240V | Residential, small business |
| Three Phase | 400V - 415V | Industrial, high-power equipment |
Advantages of Three-Phase Power
1. Cost Efficiency
When compared to single-phase power, three-phase systems are more efficient in both generation and transmission. Three-phase systems can transmit more power using fewer materials and wires, resulting in lower costs for generators and transformers.
2. Larger Power Capacity
Three-phase motors and equipment have a higher power capacity than single-phase motors, allowing them to handle larger workloads without overloading. This makes them suitable for industrial machinery, heavy equipment, and large-scale operations.
3. Stable Power Supply
With three-phase power, there is less fluctuation in the supply of electricity. This is because the three-phase system delivers a continuous flow of energy, unlike the single-phase system, where power delivery can fluctuate.
4. Improved Motor Performance
Three-phase motors offer improved performance and efficiency, consuming less energy while providing more power. This makes them ideal for machinery in industries that require constant and reliable operation.
Conclusion
A VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) is a device that controls the speed of an AC motor by adjusting the frequency of the power supplied to the motor. VFDs are used in three-phase and single-phase systems to regulate motor speed, enhance efficiency, and reduce energy consumption. By adjusting the frequency, a VFD allows for smooth control over motor operations, which is crucial for applications where varying speeds are required.






















